DNP's Display Enhancement Films: AR, AG & Retardation Films
We will elucidate the principles and applications of DNP's display enhancement films, including AR film, AG film, and retardation film.
DNP's display enhancement films function by suppressing surface reflections and minimizing glare on screens through the reduction of reflected light. The application of these films leads to a diminished impact of ambient light on LCD screens, resulting in a clearer display. In a similar fashion, retardation film finds application in OLED displays to mitigate reflections.
Beyond their use in OLED displays, the display enhancement films are extensively employed in PCs and tablet devices, establishing themselves as commonplace and well-recognized products.
*The above information is as of December, 2023.
Applications of display enhancement films
Display enhancement films find application on the upper surface of LCD TVs, PC displays, tablets, and smartphone touch panel displays. They serve as indispensable components in displays by effectively preventing glare. In the case of OLED displays, commonly featured in modern 4K TVs, a combination of retardation film and linear polarizer is employed to minimize the reflection of ambient light.

Additional applications encompass industrial displays and car navigation displays. Industrial displays are utilized in instruments for surveying, equipped with camera functions, among other uses. Even in environments where direct sunlight permeates the outdoor display, the readability is enhanced by suppressing light reflection.
Similar to other optical films designed for displays, these films must possess not only high transmittance and low haze but also exhibit scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and antifouling properties, as they are applied to the top surface.
Principle of display enhancement films
Display enhancement films are typically categorized into the following types:
AR film / LR film
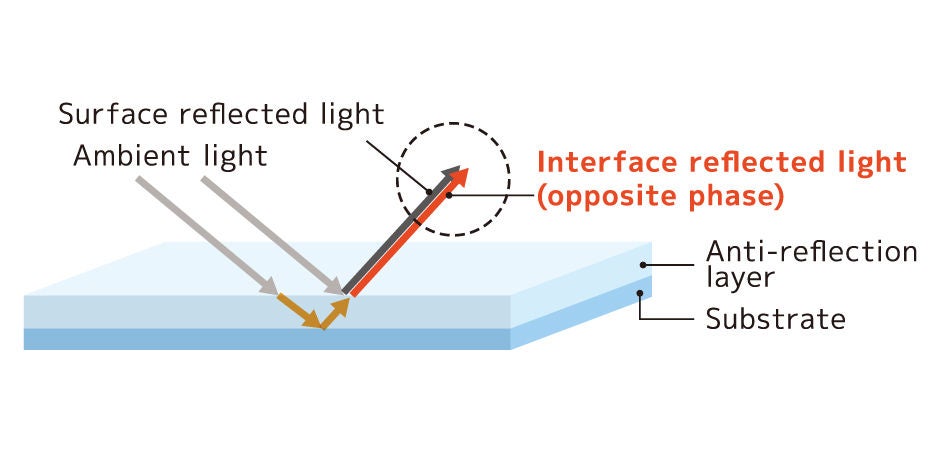
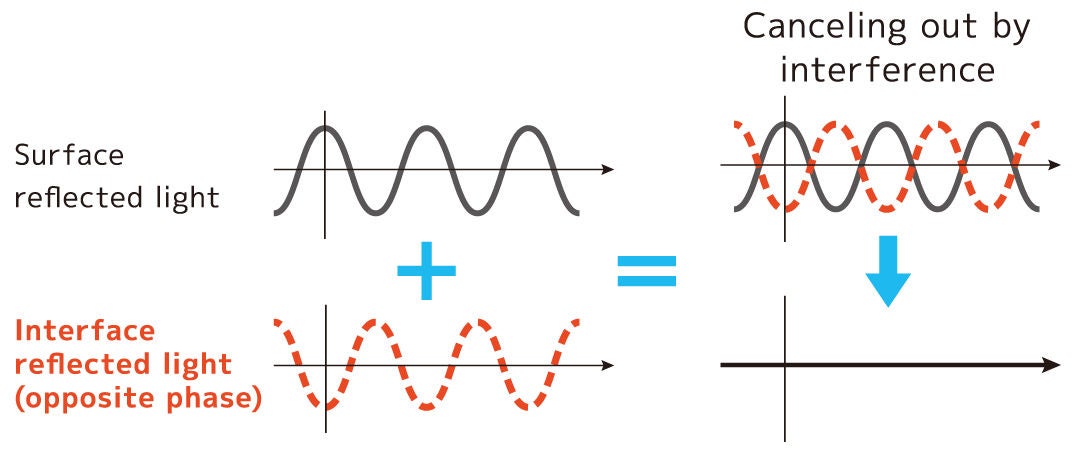
AR film or LR film (AR: Anti-Reflection, LR: Low-Reflection) constitutes an optical laminate film featuring an anti-reflection layer. The materials are meticulously designed to ensure that the light reflected on the surface of the anti-reflection layer, as well as the light transmitted through the anti-reflection layer and reflected at the interface between the anti-reflection layer and the base film, possess the same amplitude and opposite phase. This deliberate design causes interference between the two types of light, canceling each other out and thereby attenuating the reflected light, preventing it from reaching the observer's eye.
AG film
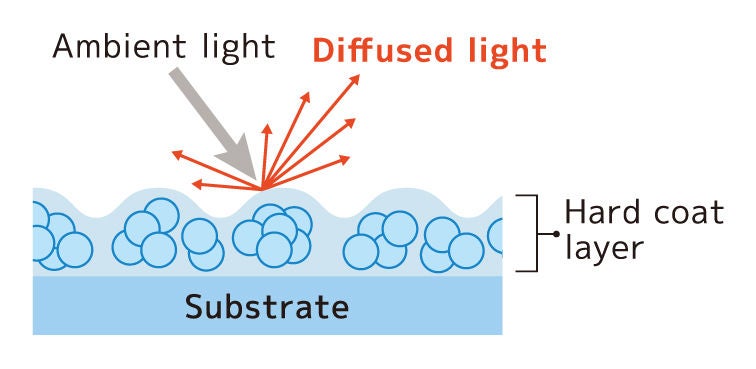
AG film (AG: Anti-Glare) is an optical laminate wherein a hard coat layer with particles is applied to the surface of a base film substrate, forming surface irregularities. Incident light is diffusely reflected on the uneven surface, effectively diminishing the glare caused by ambient light.
Retardation film
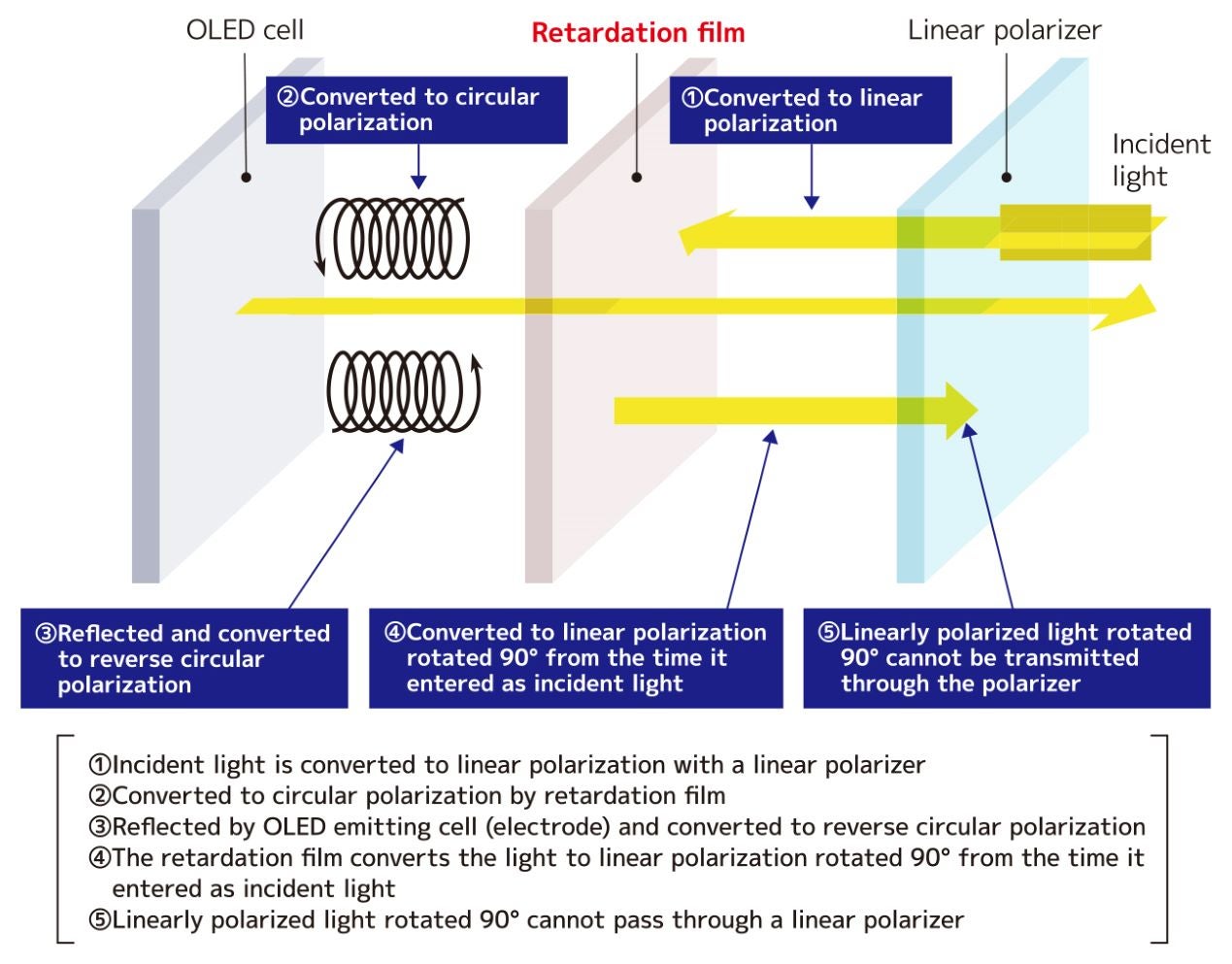
In OLED displays, a combination of retardation film and a linear polarizer is employed to mitigate the reflection of incident light onto the electrodes, thereby minimizing contrast reduction. When a retardation film and a linear polarizer are added atop the OLED panel, incoming external light (random polarization) undergoes a two-step transformation: it is initially converted to linear polarization by the linear polarizer and subsequently to circular polarization by the retardation film. The external light reflected by the electrode (OLED light-emitting cell) takes on inverse circular polarization, which is then reconverted to linear polarization through the retardation film. As the linear polarization at this stage is rotated 90° from the incident light, it cannot traverse the linear polarizer. This combined action of the linear polarizer and retardation film effectively suppresses ambient light reflection, diminishing white casts, and preventing contrast reduction.
DNP's display enhancement films
AR film

AR film (Anti-Reflection Film) employs light interference to diminish reflected light, surface reflections, and glare.
DNP's optical design technology has enabled precise control over reflectance and the reflection color that emerges during reflection.
AR film can be manufactured through various methods, including "vacuum evaporation," "sputtering/CVD," and "wet coating." DNP employs the wet coating method, known for its relatively high productivity, enabling the production of highly functional products with a reflectance as low as 0.1%, coupled with exceptional hardness.
Furthermore, DNP possesses in-house ink design technology, optimizing performance through well-balanced material blending with diverse properties, a production line capable of handling up to 2,500 mm in width, and multilayer coating technology accommodating up to three layers.
DNP manufactures AR films with diverse functionalities, including antistatic, anti-scratch, and antifouling properties.
AG film

AG film (Anti-Glare Film) is an optical laminate film featuring strategically placed particles on the surface of the base film to create surface irregularities. Utilizing AG film on the display surface enhances visibility by diffusely reflecting incident light and minimizing external light reflection.
Leveraging its accumulated technologies, DNP has refined its film design technology to effectively mitigate glare while minimizing contrast reduction resulting from diffuse reflection. Moreover, DNP has the capability to develop and manufacture tailored products that align with customer applications, including enhancements such as hardness, anti-scratch functionality, adhesiveness, and durability.
As display quality advances annually with pixels becoming increasingly refined, the irregularities of AG film become more pronounced relative to the pixels, intensifying glare-related challenges. In response to this trend, the demand for AG film with heightened brightness and superior anti-glare performance is steadily increasing. DNP is committed to continually advancing its AG film technology to deliver solutions for high-definition displays.
Retardation film

LCD and OLED displays encounter issues such as color distortion at viewing angles and diminished contrast caused by reflections from sunlight and ambient light.
The primary contributor to color shifts in LCDs is the optical shift (phase difference) that transpires when backlight illuminates the liquid crystal layer. Retardation films were devised to address this optical shift.
In OLED displays, contrast reduction arises from the reflection of external light, like sunlight, onto the electrodes. To mitigate this external light reflection, a circular polarizer, combining a linear polarizer and retardation film, is employed.
DNP applies its printing and thin-film coating expertise to fabricate retardation film using liquid crystal materials through the "coating method." The advantage of this method lies in the film's ability to be thinner than stretch-oriented retardation film. This thinness ensures flexibility, rendering it suitable for flexible OLED displays, such as those featured in foldable smartphones.
DNP for development and manufacture of display enhancement films
At DNP, we have a wealth of expertise in AR film design and manufacturing. Please contact DNP for display enhancement films. development and manufacturing. With DNP, various proposals are possible to meet your specific needs.



